Depth Sensing Beyond LiDAR Range
Kai Zhang1, Jiaxin Xie2, Noah Snavely1, Qifeng Chen2
1Cornell Tech, Cornell University 2HKUST
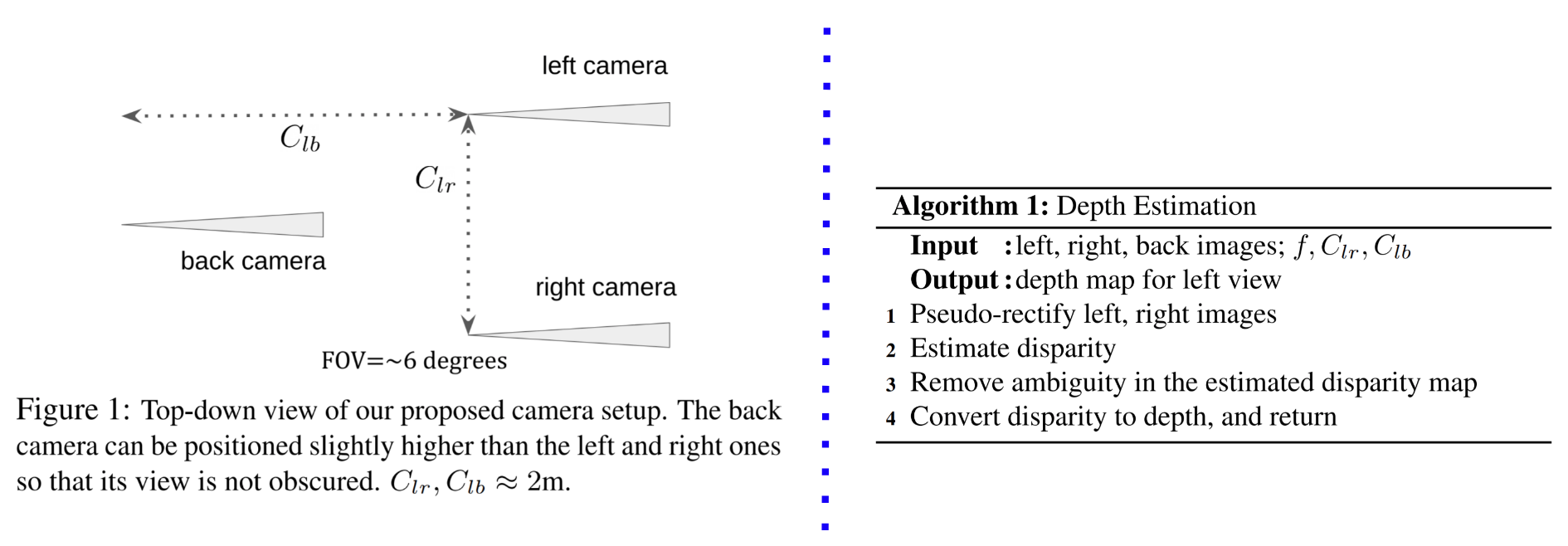
Depth sensing is a critical component of autonomous driving technologies, but today's LiDAR-based or stereo-camera-based solutions have limited range. We seek to increase the maximum range of self-driving vehicles' depth perception modules for the sake of better safety. To that end, we propose a novel three-camera system that utilizes small-FOV cameras. Our system, along with our novel processing pipeline, does not require full pre-calibration and can output dense depth maps with practically acceptable accuracy for distant scenes and objects that are not well covered by most commercial LiDARs.
We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach with both synthetic and real-world data. Experiments show that our method can achieve a 3% relative error at a distance of 300 meters in terms of depth estimation accuracy.
Paper
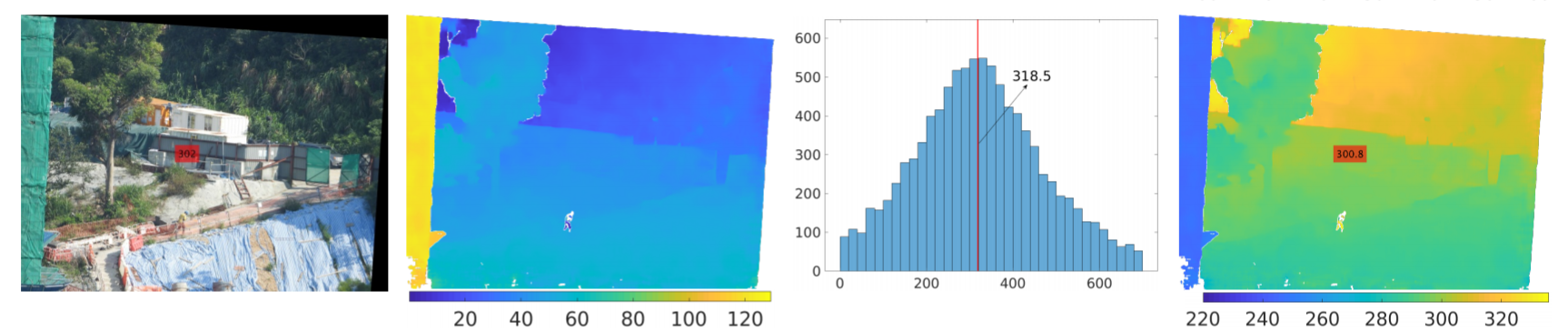
Example Result
From left to right, the four figures are pseudo-rectified left view, estimated disparity map (having an unknown offset), estimated disparity offset, final depth map (unit is meter).
The redbox on the pseudo-rectified left view marks the value (320m) acquired by a laser rangefinder, while the redbox on the final depth map marks our estimated depth (300.8m).